

These port numbers are called “ephemeral” because they are valid only for the life of the connection and have no special significance.Īn ephemeral port is a short-lived transport protocol port for Internet Protocol (IP) communications allocated automatically from a predefined range by the IP stack software. The client also needs a port number to create a TCP/IP connection, but this port number need not be well known.Ĭlients are assigned port numbers by the operating system, as part of the sequence of system calls that create a network connection. It's essential to keep in mind that the specific range for ephemeral ports may vary between different operating systems and distributions, and some applications or network configurations might require adjusting the range to better suit their needs.Ī network server process must use a “well-known” port number so that potential clients can locate it. The output will show the start and end values of the ephemeral port range, similar to the Linux command output. On Unix-based systems like macOS, you can use the following command to check the ephemeral port range: Sudo sysctl -w _local_port_range="new_start_port new_end_port" You can also modify the ephemeral port range on Linux by modifying the /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range file or by using the sysctl command: There is command you can use to know whats your current port range.Describe the significance of ephemeral and reserved port numbers.Įphemeral and Reserved Port Numbers Ephemeral port numbers

time that the ports is in " waiting" status - called the TIME WAIT - By Default - TimeWait is set to 240 sec ( thats like 4 minutes ).On a highly loaded environment, where you have hundreds of fast requests per second, you may reach a status where all ephemeral ports are either in use, or "waiting" to be released to the system, and when this happens, the application server will not be able to use them for new connectionsīut there are ways to tune the TCP/IP stack. These temporary ports will be used to handled web requests or send web reference requests, and after it's done, they will be released back to the operating system for reuse, allowing these ephemeral ports to be recycled and used by other applications or for other requests. Some ports are reserved and used by the system itself, other can't be used by other applications like port 80 for Application Server, or port 3389 for remote desktop, or ports 12000-12004 to OutSystems Services), and there's a set of ports called "ephemeral ports" that will be used by applications as temporary ports.
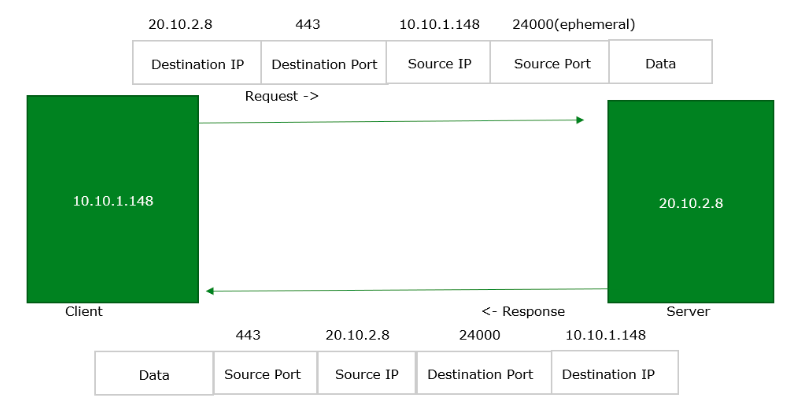
I'm talking about connection ports resources on the TCP/IP stack, because each connection will have a unique port to handle the requests, there's only 65535 ( 2^16) available ports on the system. Įphemeral port exhaustion is a resource starvation problem where a machine is no longer able to use its TCP subsystem because it does not have any available connection slots. Although the causes for such symptoms can vary - there's one scenario that can cause a complete lock of systems handling a very large number of web requests per second without any hint of what's going on: TCP/IP port exhaustion. In environments with a very high number of web requests per second, you might find that the application's performance is lower then what you would expect from that system, or even worse, the applications or web services stop responding completely or generate timeout errors, even though your system's resources (CPU, RAM or Network bandwidth) don't seem to be exhausted at all. JMeter is a wonderful tool to stress test your website and your application architecture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
